
Sustainability Materiality Assessment
The Group has conducted an in-depth analysis to identify key business materiality issues and has prioritized them into three levels of importance:
Focus Area
Ongoing
Watch List
This prioritization allows the Group to plan operations effectively and remain responsive to current and emerging situations. The process of determining important issues has been overseen by the Corporate Sustainability Management Working Group, chaired by the Group's top executive, and the Corporate Governance and Sustainable Development Committee. Sustainability goals and key performance indicators have been established to evaluate organizational outcomes and are linked to performance evaluations for the CEO and relevant employees. This integration of sustainability into performance management ensures greater awareness of the importance of sustainable development and fosters a sustainability culture throughout the organization.
In 2024, several new business materiality issues were introduced, with seven key topics added: Pollution Control and Environmental Stewardship, Access to Sustainable and Reliable Energy, Human & Labor Rights and Fair Working Conditions, Financial Sustainability and Access to Green Finance, Commitment to Quality and Continuous Improvement, Development of Renewable Energy Technology and Innovation, and Energy Reliability and Operational Efficiency. These issues align with the World Economic Forum (WEF) analysis of global sustainability trends, with the Group identifying them as critical priorities given their significant positive and negative impacts on stakeholders.
Double Materiality Issues for Business Year 2024
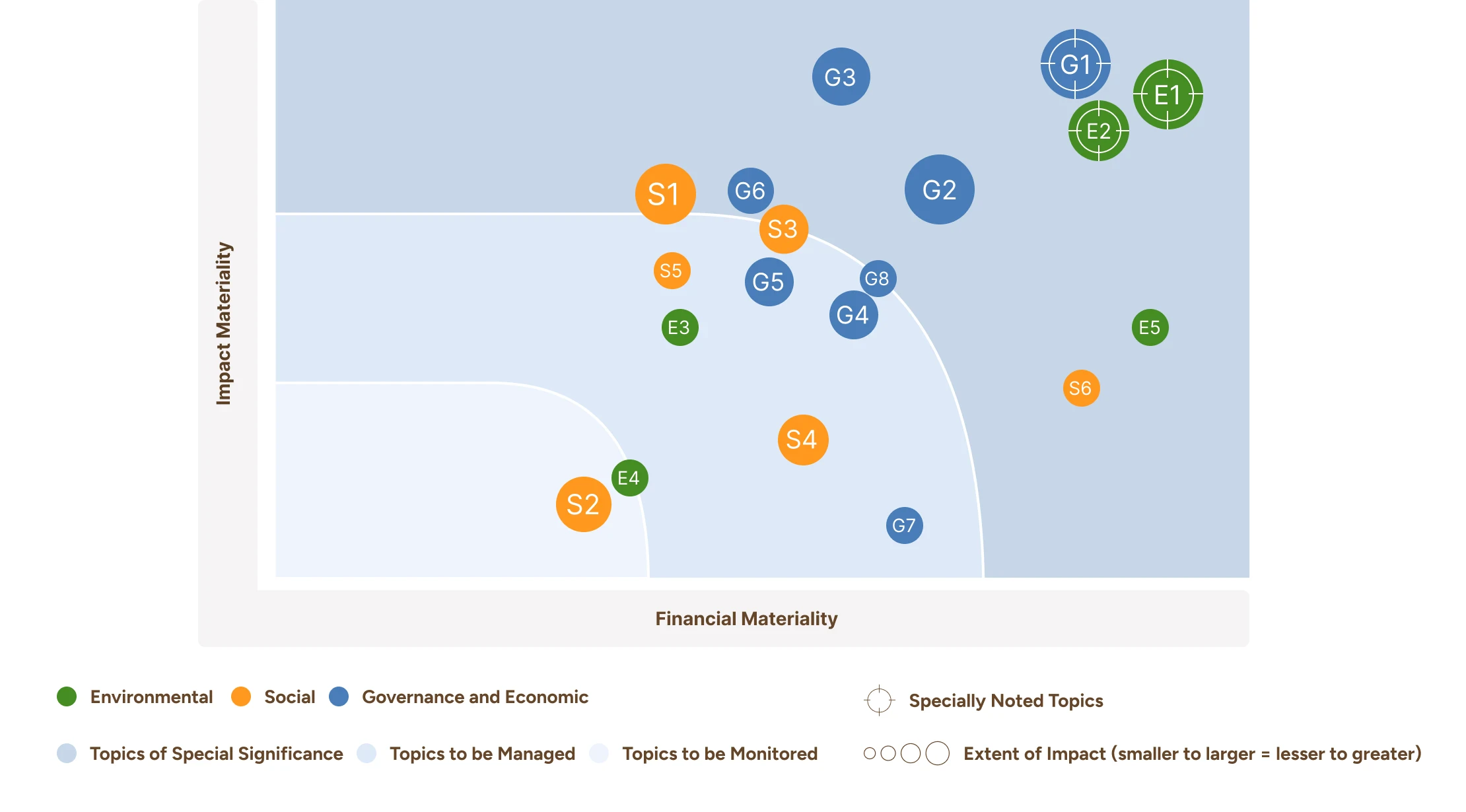
Summary of the Group's Material Issues by ESG Framework
Governance and Economic
G1
Financial Sustainability and Access to Green Finance
G2
Commitment to Quality and Continuous Improvement
G3
Transparency, Accountability, and Stakeholder Trust
G4
Development of Renewable Energy Technology and Innovation
G5
Sustainable and Responsible Supply Chain
G6
Energy Reliability and Operational Efficiency
G7
Regulatory Compliance, Standards, Ethics, Anti-Corruption, and Financial Stability
G8
Sustainable Growth and Market Expansion
Environmental
E1
Climate Change Mitigation and Resilience & Carbon and Emission Reduction
E2
Environmental Management, Resource Efficiency, and Sustainable Use
E3
Waste Management and Circular Economy
E4
Pollution Control and Environmental Stewardship
E5
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection
Social
Access to Sustainable and Reliable Energy
Customer Empowerment and Satisfaction
Empowering Human Capital for Sustainable Growth
Safety, Health, and Well-being
Community Development and Economic Empowerment
Human & Labor Rights and Fair Working Conditions
Identification of 10 Main Focus Material Topics for Business
This table can be scrolled horizontally
| Main Material Topic | Double Materiality | Importance of the Issue | Supports to the SDGs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Materiality | Financial Materiality | To the Organization | To the Economy, Society, and Environment | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identification of 7 Ongoing Material Topics for Business
This table can be scrolled horizontally
| Main Material Topic | Double Materiality | Importance of the Issue | Supports to the SDGs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Materiality | Financial Materiality | To the Organization | To the Economy, Society, and Environment | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identification of 2 Watch List Material Topics for Business
This table can be scrolled horizontally
| Main Material Topic | Double Materiality | Importance of the Issue | Supports to the SDGs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Materiality | Financial Materiality | To the Organization | To the Economy, Society, and Environment | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
